Social engineering attacks on unsuspecting employees continue to be a favorite tactic among cyberhackers. Employee behaviors, such as clicking on fraudulent links in emails, reusing passwords across business and personal accounts, or downloading PDFs containing ransomware, put a company at risk. Small to medium-sized businesses (SMB) can reduce these risks by employing the following cybersecurity best practices within their organizations.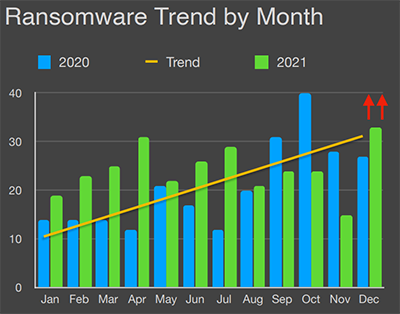 According to the latest State of Ransomware report from BlackFog, December 2021 saw the most publically reported ransomware attacks of the year, and the cybercriminals have their foot on the gas. Not only are cyberattacks trending upward, but the average size of organizations being targeted has fallen year-over-year into the SMB category.
According to the latest State of Ransomware report from BlackFog, December 2021 saw the most publically reported ransomware attacks of the year, and the cybercriminals have their foot on the gas. Not only are cyberattacks trending upward, but the average size of organizations being targeted has fallen year-over-year into the SMB category.
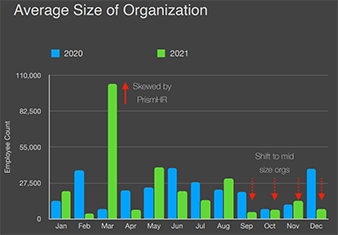 We see SMBs targeted every day and can attest that clients following recommended security best practices are materially better positioned for data breach prevention. We refer to this as “creating a culture of security”, which is the foundation of any good security strategy.
We see SMBs targeted every day and can attest that clients following recommended security best practices are materially better positioned for data breach prevention. We refer to this as “creating a culture of security”, which is the foundation of any good security strategy.
Below are five cybersecurity best practices for 2022 that will help create that culture of security, and provide practical guidance your organization can follow.
1. Implement Security Awareness Training.
Can you spot a phishing email when you see it? What do you do when you get an unexpected attachment from someone? Have you thought about how employees should handle these emails? Given the sophistication of social engineering attacks these days, it's no wonder untrained users are often tricked into doing something they otherwise would not normally do. With Security Awareness Training, you and your staff will stay up-to-date on the latest cybercriminal techniques and keep the bad guys out of your network.
2. Create Effective Cybersecurity Policies.
Security policies inform your staff on how to protect information and set the stage for defining what cybersecurity solutions you need to have in place. Without these policies specifying behavior and cybersecurity controls, we’re relying on our users to ‘make the right choice’; this can be a risky proposition. These documents become critical in the event of a security audit or even an RFP response to win new business. If you don’t have someone on staff to build the proper set of policies, it’s worth finding an expert who can help you.
3. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication.
The most recent Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report stated 85% of hacking-related breaches are due to compromised, reused, or weak passwords. Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA, is a vital cybersecurity tool in preventing data breaches due to compromised credentials (username and password). MFA supplements your password requirements, offering multiple layers of identity verification. An example of MFA is requiring a device you hold, such as a smartphone or hardware token to receive a one-time code, in addition to something you know, such as your login credentials. MFA is proven to prevent some of the most common and successful cyberattacks. Read through the Multi-Factor Authentication Guide to learn how MFA protects your business and its critical data.
4. Employ a Device Management Solution.
Device Management is how you extend the security policies you have defined to devices that are most often outside your office and used off your secure network. This can be as simple as having the ability to wipe the corporate data off of a device, or more complex like applying multiple layers of tests before letting a device connect to your network. There is a good chance you have been accessing corporate email from your smartphone for years, but you should not assume this is as secure as it would be with a device management solution.
5. Know the realities of your backups.
Backup is no longer just about the recovery of an accidentally deleted file or restoring data if your building burns down. Backup is now the best and fastest way to recover from ransomware and other cyber incidents. How much do you know about your backup and, more importantly, your recovery? How fast can you recover? How short of a time period does data go back to in the case of a recovery? Your answers to these questions will determine what the right data protections are needed for your business, the cost to implement and maintain, and what to expect should an incident occur.
Keeping your business secure is critical to success. While user behavior remains the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain, employing these cybersecurity best practices will go a long way in protecting your organization and its critical data.
If you have any questions about bolstering the cybersecurity of your organization, please call us at 888.624.6737, or email us at info@systemsengineering.com. Customers, please reach out to your Account Manager






